Spread Your Data Collection Over Days or Weeks With MicroBatch

One reason Amazon Mechanical Turk has become so popular among researchers is the speed with which data can be collected. Compared to more traditional research methods — lab-based experiments, field studies, ethnographic interviews, etc. — MTurk is exceptionally fast, making it possible to collect data for an entire study within a day or sometimes just a few hours. Although MTurk’s speed is nice, there are times when collecting data all at once can actually be a problem. In this blog, we explain how to spread your data collection out across time and why you might want to do so.
MicroBatch: A Tool For Spreading Out Data Collection
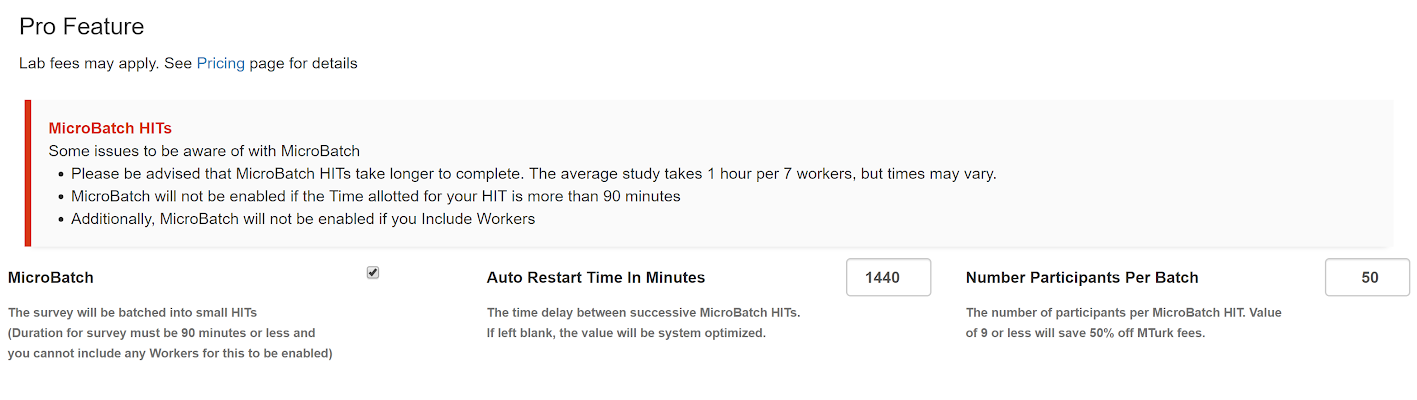
Suppose you’re running a study on MTurk and want to spread your data collection over the course of the day, several days, or even an entire week. How could you do it? If you’re only using MTurk, your options are to: a) manually setup and launch each HIT, or b) learn to write code so you can schedule various HIT launch times using MTurk’s application programming interface. Obviously, neither option is convenient. If, however, you use CloudResearch for your study, you can easily schedule HIT launch times in the study setup. Or, even better, you can use our MicroBatch feature to spread your data collection across whatever period of time you wish.
When you use MicroBatch, your study will be divided into multiple HITs of sample sizes that you chose. Rather than launching all HITs at once, MicroBatch launches one batch at a time, then restarts your study with a new batch when:
- The live batch collects all responses.
- The maximum time allowed for your batch elapses.
- When the “Auto Restart time” specified by you in the study setup elapses.
When setting up MicroBatch, you have the option to specify an Auto Restart time or allow our system to determine when your HIT should be restarted (using a combination of criteria A and B above). To really take advantage of the MicroBatch feature, it’s necessary to specify an Auto Restart Time because even studies without a specified restart time tend to collect fairly quickly (e.g., within a day).
An Example of How to Use MicroBatch
Imagine you want to run a study in which you sample 50 participants each day at 9:00am for 7 straight days. To set this study up, you would need to select MicroBatch, enter the Auto Restart Time as 1,440 minutes (24 hours x 60 minutes), and set the number of participants per batch to 50. With these options set, your study will open a HIT for 50 participants each day at 9:00am (assuming you launch your original HIT at 9:00am or schedule a study launch time). Using this simple tool, you can ensure that your data collection is spread out over a longer interval of time than if you simply launched all HITs at once.
Why Might You Want to Spread Out Data Collection?
Just as research shows there are differences in research participants across the academic semester, studies have started to show there are differences in online samples across time of day. People who participate in online studies in the morning sometimes have a different personality profile than those who participate in the evening (Arechar, Kraft-Todd, & Rand, 2017). Furthermore, participants can vary based on the day of the week they participate or even whether they participate earlier or later in your data collection (e.g., Casey, Chandler, Levine, Proctor, & Strolovitch, 2017). Using MicroBatch, you can spread out your data collection to ensure a more representative sample.
A Few Notes About MicroBatch
Because MicroBatch relies on the ability to restart your HIT, there are some instances in which MicroBatch cannot be used. For example, when the Time allotted per assignment for your study is set to more than 90 minutes, MicroBatch is not available. In addition, MicroBatch cannot be used for studies in which you use some type of Include list to specify workers who are eligible for the HIT. In both of these instances, features of your study (time allowed or workers to be included) interferes with the restart function, making MicroBatch unavailable.
References
Arechar, A. A., Kraft-Todd, G. T., & Rand, D. G. (2017). Turking overtime: How participant characteristics and behavior vary over time and day on Amazon Mechanical Turk. Journal of the Economic Science Association, 3, 1-11.
Casey, L. S., Chandler, J., Levine, A. S., Proctor, A., & Strolovitch, D. Z. (2017). Intertemporal differences among MTurk workers: Time-based sample variations and implications for online data collection. SAGE Open, 7, 2158244017712774.

